Development of Virtual Reality Training System for steel mill facility
Eeljin Chae1, Junho Lee2, Hosung Myung3
1Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, China Korea School of New Media
182# Nanhu Ave., East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan
Hubei, China
cinetree@dongseo.ac.kr,
2DAVID LINE STUDIO,
726 PENDIO, IRVINE, .
CA, United States
davidlinelee@gmail.com
3Shanghai Univ. of Engineering Science, Sino-Korean School Multimedia Design
333 Long Teng Road
Shanghai, China
mhs0825@nate.com
Abstract
Virtual work exercise using Virtual Reality (VR) technology can acquire experiences similar to actual work atmosphere, it has better learning immersion and effectiveness than existing a traditional e-learning and an ordinary video education material. This virtual reality safety education content is created for B steel, one of best steel company in China, the movement of steel equipment that is generally inaccessible and dangerous, such as cold-rolled coil packaging process. For education contents applied with virtual reality technology, it is necessary to research learner's perspective on the application of technology from is needed, such as the quality of content and the number of frames per second that can minimize VR motion sickness, in addition to quality and effectiveness of the teaching contents. In this study, we are going to describe how virtual reality educational contents are implemented for the "cold rolled coil shearing line in the steel mill."
Keywords; VR;safety education;steel mill
1. Introduction
Virtual Reality (VR) technology is a
technology that provides a sense of reality and immersion to humans through a
three-dimensional virtual environment that is sampled by computers. In other
words, its effectiveness is demonstrated in a wide variety of areas, such as education/
medical/ manufacturing/ aeronautics/ military/ entertainment based on visualizations
of data. [1] Simulation VR educational content that mitigates natural
disasters, firefighting safety, and extreme anxiety already has a number of
examples to consider qualitative levels.
Virtual work education content can produce experiences similar to actual work
experience and is seen as an alternative to expensive lab equipment with no
time and space limitations in education. No virtual reality (VR) based virtual
work experience content has been developed yet in the field of steelmaking. The
real knowledge is derived from the practitioner’s own experience in the process
of learning and the actual
acting.[2] “The knowing is in
the action. It is revealed by the skillful execution of the performance – we
are characteristically unable to make it verbally explicit.” [3]
The Sino-Korean School Multimedia Design has planned to develop safety education contents and operational training materials for crane facilities that are at high risk so as to result in death of accidents caused by safety insensitivity. In total, 14 experts and student’s assistance have developed and produced this safety education VR material for three months with the aid of B steel, China's largest steelmaker by supporting its’ basic materials.
VR-based simulation training content for natural hazards (e.g. earthquake, tidal waves, typhoons, wildfires, etc.) is developed in the following procedure; Data analysis and scenario design → 3D modeling (props, character, and environmental modeling data) → Development of simulation technology and interactive technology → Sound effect and music → Prototype of virtual reality S/W and H/W in Head Mounted Display → Completion of educational content development.
In particular, real-time visualization technology, interface technology for interaction, and integrated with simulation operational technologies that are based on a variety of engineering disciplines. This project is a safety training content for facility operation other than simulators, so the simulator interaction function was excluded in this paper. Recently, as the safety awareness of facility operation has increased, the necessity of safety education content at each site is has raised. However, it is difficult to find contents about a crane operation tutorial for the efficiency and a safety training manual for the effectiveness in the steel mill.[4] In fact, it is necessary to apply educational content that utilizes virtual reality technology at a site where high-cost crane must not be used only for education. The internal data provided by B steel shows that the movement of heavy and bulky materials on the factory often leads to employee’s death in the event of an accident. Therefore, the purpose of this development is to eliminate the insensitivity to safety by actively utilizing the content developed in advance training of the operation of the crane by field staff.
2. Development Procedure
2.1. Analysis and planning
As "virtual reality (VR) based steel mill crane safety education contents" were targeted at new employees or operators at a steel mill, many jargon and abbreviations were used. Multimedia experts and B steel company collaborated to develop this scenario to let field employee train the safety education and operate equipments practically. In other words, we learn how to control equipments properly while the collision and collaboration occurs. The scope of development designate two parts; 1.Prevention of safety accidents during crane operation, 2.Cooling coil packaging process. On planning stage, we analyzed the relevant data carefully, designed for data survey on the facility (Table. 1). Thus they obtained maximum realism on the scenario considering the VR environment and the vivid and real situation to have monitored on site several times to record the actual noise and ambient sound in the steel mill.
Table. 1 Training contents Scenario
|
Scene |
Screen |
Scenario |
|
#01 start |
|
1. Introduction 2. VR interface drill 3. Lobby enter |
|
#02 lobby |
|
1. Main facility and equipment Hall 2. Safety education video 3. Equipment operation exercise video 4. Wear a safety helmet and enter the training site
|
|
#03 factory |
|
1. A safety training exercise that reproduces the actual crane collisions and stenosis deaths. 2. Practice of operating the wireless remote control for crane operation 3. Practice on cold-rolled coil packaging process |
2.2. Modeling
We checked in advance the list of 3D objects based on photos of site facilities and cases of safety accidents provided by the B steel. Afterwards it took us about 10 weeks carrying out the modeling 3D objects by using UNITY, 3ds Max, based on actual measurement data, in the same form as the actual crane installation. When selecting objects for 3D modeling required for precision inspection training contents and carrying out 3D modeling such as indoor environment for buildings with corresponding facilities and tools for precision inspection, the results are shown in Figure. 1.
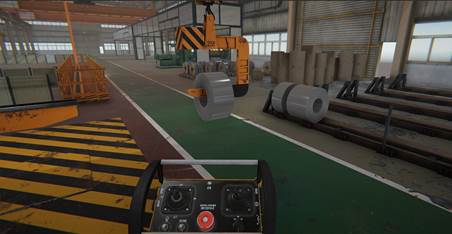
Fig. 1 3D Modeling objects and data of steel mill
2.3. Learning contents development
The optimization of modeling data was time consuming to convert 3ds Max data into graphic data formats in game engines, as the development target cold rolled coin shearing packaging facility had to express both exterior and interior structures. The training content was developed using the game engine Unity 3D, and the motion sensor was developed under the VIVE HMD that can express sufficient spatiality and movement by using two sensors over Oculus, which limits the range of motion with one sensor as shown in Fig. 2. The system is configured to minimize VR motion sickness by configuring HD quality above 2K and 120 frames per second.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) VR interface, GUI |
(b) VR interaction |
(c) Demo screenng |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Safety contents |
(e) On site Practice |
(f) Facility operation practice |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 2 3D Modeling objects and data for training contents
2.4. Interaction technology development
You should left- and right-justify your columns. On the last page of your paper, try to adjust the lengths of the two columns so that they are the same. Use automatic hyphenation, if you have it. Don't forget to check the spelling.
The cold rolled coin shearing packaging process executes a precision inspection in real time for safety accidents by moving the facilities in a wide range of spaces. We considered this characteristic wide range moving the functions of the crane controller were established in the form of pulling or pushing the facility towards the center of the trainee.
Considering that most of the participants are not experienced in using virtual reality (VR) devices, we designed the learner should recognize their behavior. We divided the selection button on the controller left( tools selection/ parts selection/ valve operation/ bolt tightening) and the on/off button on the controller right (start/ stop).
2.5. Safety education contents development and sound effect
You should left- and right-justify your columns. On the last page of your paper, try to adjust the lengths of the two columns so that they are the same. Use automatic hyphenation, if you have it. Don't forget to check the spelling.
"Safety training content for cold rolled coin shearing packaging process" is provided to the users on the left, and various tools to be used for inspection are displayed on the right, as the controller shown in Figure. 1.
We completed the introduction sound that can be heard in a space where cold rolled coin shearing packaging process crane facilities are installed, the sound and narration corresponding to each precision inspection phase and warning/notification/calibration are applied.
3. Conclusion
This paper provides the process of developing contents to enhance safety awareness in order to develop VR contents platform for safety education in the case of B steel crane operation. This platform provides a new interaction paradigm and requires users to learn how to use it efficiently. According to a recent survey of Korea's VR industry, the competitive edge of education contents compared to overseas markets was 4.13 points out of 7 point.[5] While VR education contents have already been commercialized, Medical and automotive and manufacturing sectors, the field of safety education is currently applied to the field. The newly developed product will be installed at the VR Showroom in the B-steel headquarters. In the future, it is necessary to import raw materials from which coils are generated in and to develop hardware that is actually linked to the entire process from rolling, reprocessing and packaging. Starting with this "Safety Education Content for Packaging Process", it is expected that variety of contents and VR-based educational contents will be produced.
References
[1] Jeon Hang-soo, "Trend of applies to VR’s global and domestic market" Electronic Communication Trend Analysis, Vol. 32 pp.98-99, 2017.
[2] P. Lévy and R. Bononno, “Becoming virtual: Reality in the digital age”. Da Capo Press, Incorporated, 1998.
[3] Schön, Donald, “The Reflective practitioner.” New York Basic Books, Inc., Publishers, 1983.
[4] A. Langley,G. Lawson,S. Hermawati,M. D’Cruz,J. Apold,F. A r l t and K. Mura, “Establishing the Usability of a Virtual Training System for Assembly Operations within the Automotive Industry” Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing & Service Industries, Vol. 26, pp.667-679, 2016.
[5] Seungpyo Hong, "A survey on the VR Industry in Korea," Institute for Information and Communications Technology Promotion, pp.24, 2016.










